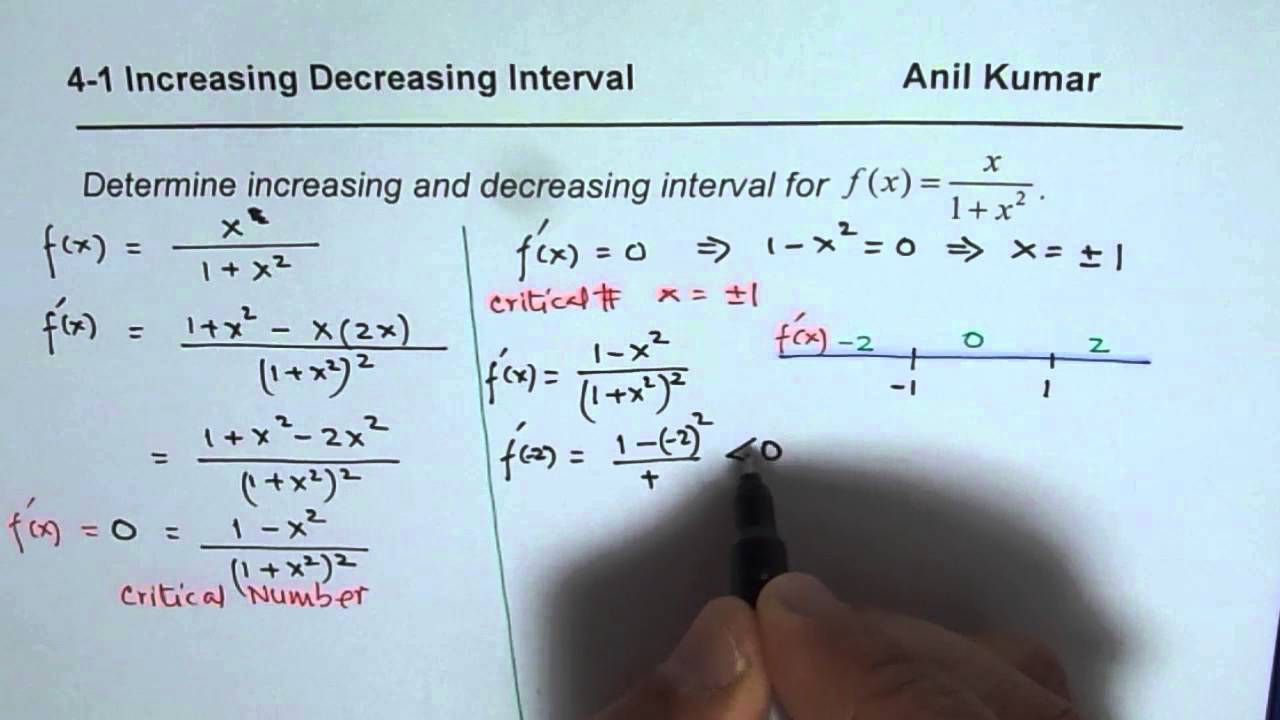
Find The Intervals On Which F Is Increasing And Decreasing . List the intervals on which the function is increasing and decreasing. $ f(x) = \frac{x}{x^2 + 1} $
Use A Graph To Determine Where A Function Is Increasing, Decreasing, Or Constant | College Algebra from courses.lumenlearning.com
So hopefully that gives you a sense of things. Ponder the graphs in the box above until you are confident of why the two conditions listed are true.
Use A Graph To Determine Where A Function Is Increasing, Decreasing, Or Constant | College Algebra
(a) find the intervals on which f is increasing or decreasing. If f' (c) > 0 for all c in (a, b), then f (x) is said to be increasing in the interval. (a) find the intervals on which $ f $ is increasing or decreasing.
Source: www.chegg.com
If 𝑓 is differentiable on an open interval, then 𝑓 is increasing on intervals where 𝑓 ′ ( 𝑥) > 0 and decreasing on intervals where 𝑓 ′ ( 𝑥) 0.in the graph above, the graph increases over the part that is.know how to use the rst and second derivatives of a function to nd intervals on which the function.
Source: www.nagwa.com
This is the currently selected item. To find increasing and decreasing intervals, we need to find where our first derivative is greater than or less than zero.to find intervals on which \(f\) is increasing and decreasing:to find the an increasing or decreasing interval, we need to find out if the first derivative is positive or negative on the given interval..
Source: www.chegg.com
The original function f is increasing on the intervals for which f ′ ( x) > 0, and decreasing on the intervals for which f ′. The intervals where a function is increasing (or decreasing) correspond to the intervals where its derivative is positive (or negative). Recall that, if f ' > 0 on a given interval, then f is.
Source: www.youtube.com
Find the intervals on which f is increasing or decreasing. Notice, these aren't the same intervals. That we are, the intervals where we're positive or negative don't perfectly coincide with when we are increasing or decreasing.
Source: www.nagwa.com
So hopefully that gives you a sense of things. If f ′ ( x) < 0 on an open interval, then f is decreasing on the interval. The intervals where a function is increasing (or decreasing) correspond to the intervals where its derivative is positive (or negative).
Source: www.nagwa.com
Evaluate the derivative at a point in each subinterval to determine. Analytically, we find these intervals using the following process: If f' (c) < 0 for all c in (a, b), then f (x) is said to be decreasing in the interval.
Source: www.youtube.com
F(𝑥) = sin 3𝑥 where 𝑥 ∈ [0 ,𝜋/2]finding f’(x)f’(𝑥) = 𝑑(sin3𝑥 )/𝑑𝑥 f’(𝑥) = cos 3𝑥 × 3 f’(𝒙) = 3. So if we want to find the intervals where a function increases or decreases, we take its derivative an analyze it to find where it’s positive or negative (which is easier to do!). (b) find the local maximum.
Source: mathematica.stackexchange.com
The original function f is increasing on the intervals for which f ′ ( x) > 0, and decreasing on the intervals for which f ′. Find the intervals in which `f (x)=s in\ x (1+cosx),\ \ 0<x<pi/2` is increasing or decreasing: (a) find the intervals on which $ f $ is increasing or decreasing.
Source: www.khanacademy.org
(b) find the local maximum and minimum values of f. Example 12 find intervals in which the function given by f (x) = sin 3x, x, ∈ [0, 𝜋/2] is (a) increasing (b) decreasing. If f' (c) = 0 for all c in (a, b), then f (x) is said to be constant in the interval.
Source: www.slideshare.net
Determining intervals on which a function is increasing or decreasing. Finding increasing interval given the derivative. Analytically, we find these intervals using the following process:
Source: www.youtube.com
List the intervals on which the function is increasing and decreasing. Find the intervals in which `f (x)=s in\ x (1+cosx),\ \ 0<x<pi/2` is increasing or decreasing: If f(x) > 0, then the function is increasing in that particular interval.
Source: www.youtube.com
$ f(x) = \sin x + \cos x $, $ 0 \leqslant x \leqslant 2\pi $ The part of the graph corresponding to this interval is also shown. So f of x is decreasing for x between d and e.
Source: www.chegg.com
Recall that, if f ' > 0 on a given interval, then f is increasing on that interval, and when f ' < 0 on a given interval, then f is decreasing on that interval. That we are, the intervals where we're positive or negative don't perfectly coincide with when we are increasing or decreasing. The function is increasing on.
Source: www.nagwa.com
(b) find the local maximum and minimum values of f. Find the intervals on which f is increasing or decreasing. (a) find the intervals on which $ f $ is increasing or decreasing.
Source: www.chegg.com
Determining intervals on which a function is increasing or decreasing. (c) find the intervals of concavity and the inflection points. That we are, the intervals where we're positive or negative don't perfectly coincide with when we are increasing or decreasing.
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
(b) find the local maximum and minimum values of $ f $. If f(x) > 0, then the function is increasing in that particular interval. The part of the graph corresponding to this interval is also shown.
Source: study.com
Example 12 find intervals in which the function given by f (x) = sin 3x, x, ∈ [0, 𝜋/2] is (a) increasing (b) decreasing. To find increasing and decreasing intervals, we need to find where our first derivative is greater than or less than zero.to find intervals on which \(f\) is increasing and decreasing:to find the an increasing or decreasing.
Source: www.cuemath.com
We use this test in several ways. So if we want to find the intervals where a function increases or decreases, we take its derivative an analyze it to find where it’s positive or negative (which is easier to do!). (a) find the intervals on which $ f $ is increasing or decreasing.
Source: www.khanacademy.org
If 𝑓 is differentiable on an open interval, then 𝑓 is increasing on intervals where 𝑓 ′ ( 𝑥) > 0 and decreasing on intervals where 𝑓 ′ ( 𝑥) 0.in the graph above, the graph increases over the part that is.know how to use the rst and second derivatives of a function to nd intervals on which the function.
Source: www.chegg.com
So f of x is decreasing for x between d and e. F(𝑥) = sin 3𝑥 where 𝑥 ∈ [0 ,𝜋/2]finding f’(x)f’(𝑥) = 𝑑(sin3𝑥 )/𝑑𝑥 f’(𝑥) = cos 3𝑥 × 3 f’(𝒙) = 3. Finding intervals of increasing and decreasing.